2026 World Cup hosting cities: Get ready for a global football fiesta! Three nations – the USA, Canada, and Mexico – are jointly hosting the tournament, promising a unique and expansive experience for players and fans alike. Imagine the electrifying atmosphere in state-of-the-art stadiums across North America, the vibrant cultural exchanges between diverse cities, and the sheer scale of this unprecedented event.
This exploration delves into the exciting details of each host city, examining their infrastructure, economic prospects, and the captivating cultural impact this mega-event will undoubtedly have.
From the bustling metropolises to the vibrant cultural hubs, each city brings its own unique flavor to the tournament. We’ll uncover the logistical challenges and advantages of this geographically diverse hosting arrangement, considering the potential impact on travel, fan experience, and team preparation. We’ll also explore the environmental sustainability plans, security measures, and the projected economic booms expected in each host city.
Buckle up, because this journey into the heart of the 2026 World Cup is about to kick off!
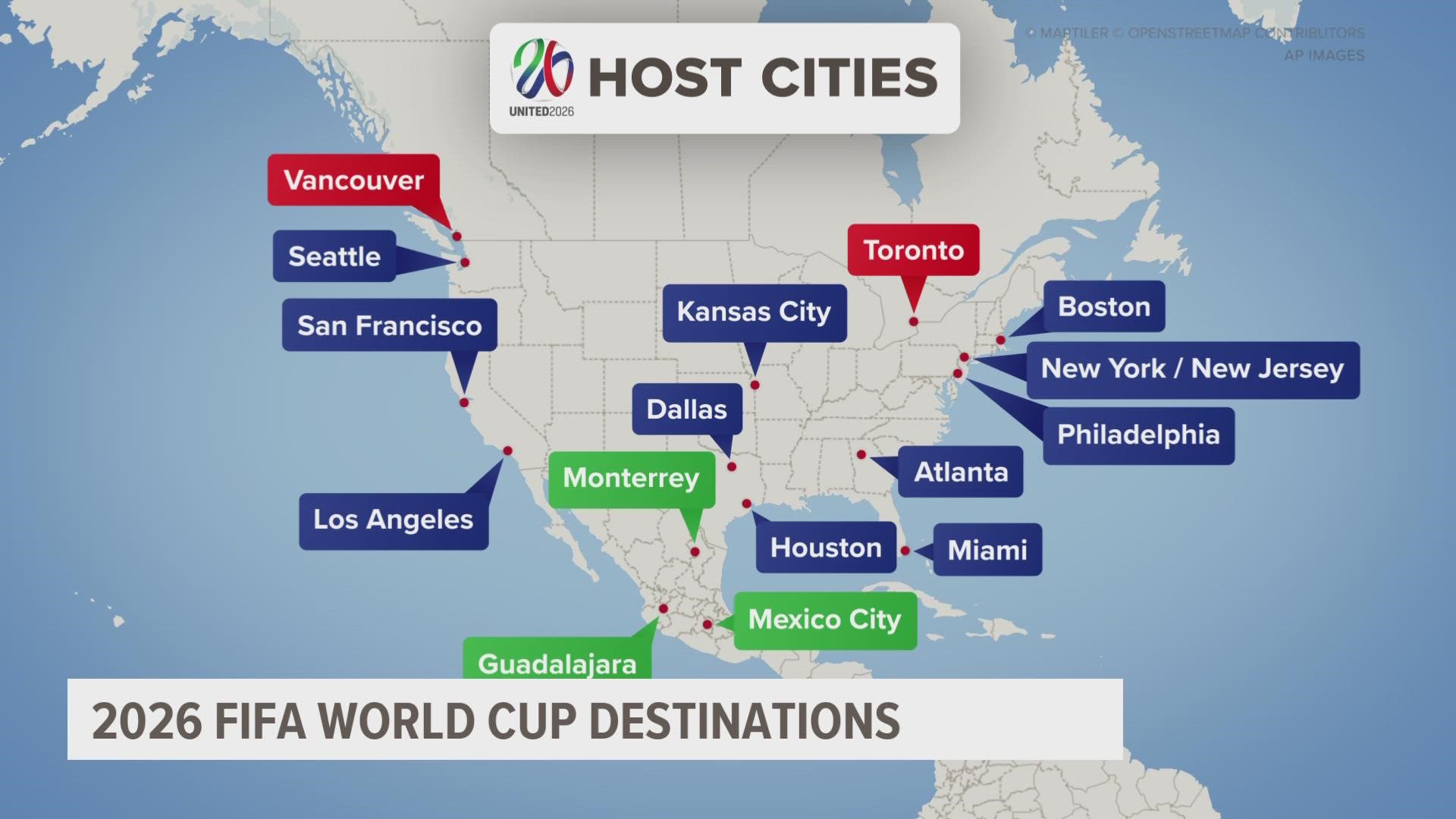
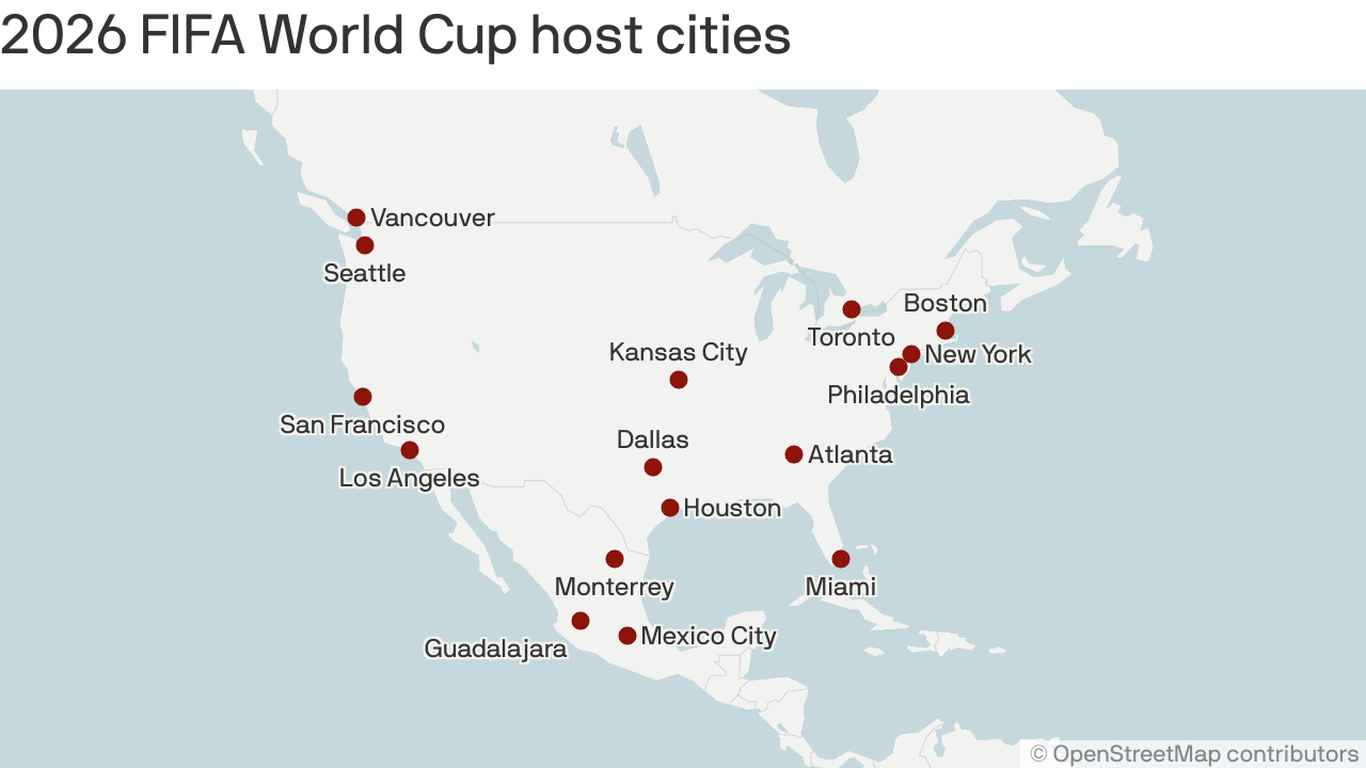
Geographical Distribution of Host Cities: 2026 World Cup Hosting Cities
The 2026 FIFA World Cup, a joint venture between the United States, Mexico, and Canada, presents a unique geographical challenge and opportunity. The vast distances separating the host cities across three nations necessitate careful logistical planning to ensure a smooth and efficient tournament. This geographical spread, however, also offers the potential to showcase the diverse cultures and landscapes of North America to a global audience.The geographical distribution of the host cities is visually striking.
Imagine a map of North America. You would see a cluster of cities along the eastern coast of the United States, extending from Boston in the north to Atlanta in the south. Further west, you’d find cities like Dallas and Kansas City. Mexico contributes cities such as Mexico City, Guadalajara, and Monterrey, positioned centrally in the country.
Finally, Canada adds Toronto and Vancouver, representing the country’s eastern and western extremes. This spread, while geographically extensive, is not uniform, with significant concentrations in the US.
Logistical Challenges and Advantages of Geographical Spread
The vast distances between host cities present significant logistical challenges. Transportation of teams, officials, and equipment will require meticulous planning and substantial resources. The potential for travel delays due to weather or other unforeseen circumstances needs to be mitigated through contingency planning. Furthermore, coordinating security efforts across such a wide area requires substantial inter-agency collaboration and coordination.
However, the geographical spread also offers advantages. It allows for a wider distribution of economic benefits across the three host nations, stimulating local economies in various regions. The diverse landscapes and cultural experiences offered by each host city provide a richer and more varied experience for fans and players alike. This diversity could lead to increased tourism and a more memorable World Cup experience.
Impact of Travel Time and Costs on Fans and Teams
The significant distances between host cities will undoubtedly impact travel time and costs for both fans and teams. Fans planning to attend multiple matches may face long and expensive journeys between venues. For example, a fan traveling from Vancouver to Guadalajara would experience a considerable journey, potentially requiring multiple flights and significant financial investment. This could potentially limit fan attendance at matches outside their immediate geographical area.
Similarly, teams will face logistical challenges in managing travel between matches, impacting player recovery time and potentially affecting team performance. The costs associated with these journeys will be substantial for both teams and fans, requiring careful budgeting and planning. The tournament organizers will need to consider strategies to mitigate these impacts, such as providing affordable travel options or offering incentives to encourage attendance across various locations.
Find out further about the benefits of how often is a world cup that can provide significant benefits.
The experience of the 2007 Rugby World Cup, held across several cities in France, serves as a case study. While the logistical challenges were substantial, the economic benefits and overall positive impact of the event ultimately outweighed the challenges.
Economic Impact on Host Cities
The 2026 FIFA World Cup promises a significant economic boost for the host cities, but also presents potential challenges. This section delves into the projected economic benefits, potential risks, and comparisons with previous World Cup events to offer a comprehensive overview of the financial implications for each participating city. We will explore both the positive and negative aspects, providing a balanced perspective on the economic reality of hosting such a massive global event.
Projected Economic Benefits
Hosting the World Cup is expected to generate substantial economic benefits for each host city through increased tourism and infrastructure development. These benefits are multifaceted, encompassing direct spending by visitors, increased employment opportunities, and long-term infrastructure improvements that enhance the city’s appeal and functionality. For example, the 2014 World Cup in Brazil saw significant increases in tourism revenue in host cities, even though some infrastructure projects faced delays and cost overruns.
Similarly, the 2018 World Cup in Russia spurred significant investment in transportation and hospitality infrastructure, leaving a lasting legacy for those cities. Specific projected figures for each 2026 host city require detailed economic modeling based on factors such as expected tourist numbers, ticket sales, and media coverage, which is beyond the scope of this overview. However, it’s safe to assume that cities like New York, Los Angeles, and Mexico City are projected to see substantially higher economic gains than smaller cities due to their existing tourism infrastructure and larger populations.
Potential Challenges and Risks
While the economic benefits are significant, hosting the World Cup also involves substantial financial burdens and risks. These include the initial investment in infrastructure upgrades, the operational costs of hosting matches and related events, and the potential for unforeseen expenses and cost overruns. The risk of inadequate planning or mismanagement leading to financial losses is a real concern, as seen in some past World Cups.
For instance, some South African cities struggled to fully capitalize on the economic opportunities presented by the 2010 World Cup due to logistical challenges and a lack of sufficient planning for post-tournament legacy projects. Furthermore, security costs, potential disruptions to normal city operations, and the possibility of lower-than-expected tourism can all negatively impact the financial outcome. A robust risk assessment and comprehensive financial planning are crucial to mitigate these potential challenges.
Comparison with Previous World Cup Experiences, 2026 world cup hosting cities
Analyzing the economic impact of previous World Cups provides valuable insights into the potential outcomes for the 2026 event. While each World Cup is unique, considering past experiences allows for more accurate predictions and better preparedness. The 2006 World Cup in Germany, for example, demonstrated the potential for significant long-term economic benefits, with sustained growth in tourism and related industries.
Conversely, the 2014 World Cup in Brazil, despite its immense popularity, faced criticism regarding the management of public funds and the sustainability of infrastructure projects. A detailed comparative analysis, considering factors like pre-existing infrastructure, tourism levels, and government investment strategies, is crucial for accurate forecasting and effective resource allocation for the 2026 host cities. This comparison should inform the development of realistic expectations and effective strategies to maximize the economic benefits while minimizing potential risks.
Environmental Considerations

The 2026 FIFA World Cup presents a unique opportunity to showcase environmental sustainability on a global stage. Host cities are embracing this challenge, implementing various initiatives to minimize the tournament’s ecological footprint and leave a positive legacy. This section details the planned sustainability measures, potential environmental challenges, and mitigation strategies being employed.
Sustainable Transportation Initiatives
Many host cities are prioritizing sustainable transportation options to reduce carbon emissions associated with fan travel and logistical operations. This involves expanding public transportation networks, promoting the use of electric vehicles, and encouraging cycling and walking. For example, a city might invest in a new light rail system connecting stadiums and fan zones, complemented by dedicated cycling lanes and pedestrian walkways.
This integrated approach aims to minimize reliance on private vehicles and reduce traffic congestion, improving air quality simultaneously.
Waste Management and Recycling Programs
Effective waste management is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of a large-scale event like the World Cup. Host cities are implementing comprehensive recycling and waste reduction programs, including the use of reusable materials, composting initiatives, and waste sorting facilities at stadiums and fan zones. The goal is to divert a significant portion of waste from landfills and promote a circular economy model.
For instance, a city might partner with local recycling companies to ensure efficient processing of recyclable materials collected during the tournament. This could include initiatives to educate fans on proper waste disposal and the benefits of recycling.
Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Sources
Minimizing energy consumption and transitioning to renewable energy sources are key components of the environmental sustainability plan. Host cities are exploring options such as installing solar panels on stadiums and other infrastructure, utilizing energy-efficient lighting and appliances, and investing in smart grid technologies. The aim is to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and minimize greenhouse gas emissions. For example, a stadium might incorporate solar panels into its roof design, generating a portion of its energy needs from renewable sources.
Furthermore, the use of LED lighting throughout the venues can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional lighting.
Water Conservation Strategies
Water scarcity is a growing concern in many parts of the world, and the World Cup is taking steps to address this issue. Host cities are implementing water conservation measures, such as using water-efficient landscaping, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater recycling. The goal is to minimize water consumption and reduce the tournament’s overall water footprint. A city might, for example, install rainwater harvesting systems at stadiums to collect rainwater for irrigation purposes, reducing the need for municipal water supplies.
Similarly, greywater recycling systems can reuse water from showers and sinks for non-potable purposes like irrigation.
Mitigation Strategies for Potential Environmental Challenges
Despite proactive measures, potential environmental challenges remain. These include increased air pollution from transportation, waste generation, and potential impacts on local ecosystems. Mitigation strategies include stringent air quality monitoring, enhanced waste management programs, and environmental impact assessments to minimize negative effects on biodiversity and natural habitats. For instance, a city might conduct thorough environmental impact assessments before and during construction projects, ensuring minimal disruption to local ecosystems.
They could also implement air quality monitoring systems to track pollution levels and adjust transportation plans accordingly. Furthermore, the use of sustainable construction materials and practices during stadium renovations and construction minimizes the environmental impact of building projects.
The 2026 World Cup promises to be more than just a football tournament; it’s a celebration of global unity, cultural exchange, and sporting excellence. The diverse range of host cities, each with its unique character and infrastructure, ensures a truly unforgettable experience for fans and players alike. From the economic benefits to the social and environmental impacts, the legacy of this tournament will resonate for years to come.
So, mark your calendars, book your flights, and prepare for an incredible journey across North America – the 2026 World Cup is coming!